Simulate a simple matrix or SingleCellExperiment to test internals of scMerge
Source:R/ruvSimulate.R
ruvSimulate.RdThis function is designed to generate Poisson-random-variable data matrix to test on the internal algorithms of scMerge. It does not represent real biological situations and it is not intended to be used by end-users.
ruvSimulate(
m = 100,
n = 5000,
nc = floor(n/2),
nCelltypes = 3,
nBatch = 2,
k = 20,
lambda = 0.1,
sce = FALSE
)Arguments
- m
Number of observations
- n
Number of features
- nc
Number of negative controls
- nCelltypes
Number of cell-types
- nBatch
Number of batches
- k
Number of unwanted factors in simulation
- lambda
Rate parameter for random Poisson generation
- sce
If
TRUE, returns a SingleCellExperiment object
Value
If sce is FALSE, then the output is a list consists of
Y, expression matrix generated through Poisson random variables,
ctl, a logical vector indicating the control genes,
M, replicate mapping matrix,
cellTypes, a vector indicating simulated cell types
batch, a vector indicating simulated batches
if sce is TRUE, a SingleCellExperiment wrapper will be applied on all above simulated objects.
Examples
set.seed(1)
L = ruvSimulate(m = 200, n = 1000, nc = 200,
nCelltypes = 3, nBatch = 2, lambda = 0.1, k = 10, sce = TRUE)
print(L)
#> class: SingleCellExperiment
#> dim: 1000 200
#> metadata(1): M
#> assays(2): counts logcounts
#> rownames(1000): gene1 gene2 ... gene999 gene1000
#> rowData names(0):
#> colnames(200): cell1 cell2 ... cell199 cell200
#> colData names(2): cellTypes batch
#> reducedDimNames(0):
#> mainExpName: NULL
#> altExpNames(0):
example <- scMerge(sce_combine = L,
ctl = paste0('gene', 1:500),
cell_type = L$cellTypes,
ruvK = 10,
assay_name = 'scMerge')
#> Dimension of the replicates mapping matrix:
#> [1] 200 3
#> Step 2: Performing RUV normalisation. This will take minutes to hours.
#> scMerge complete!
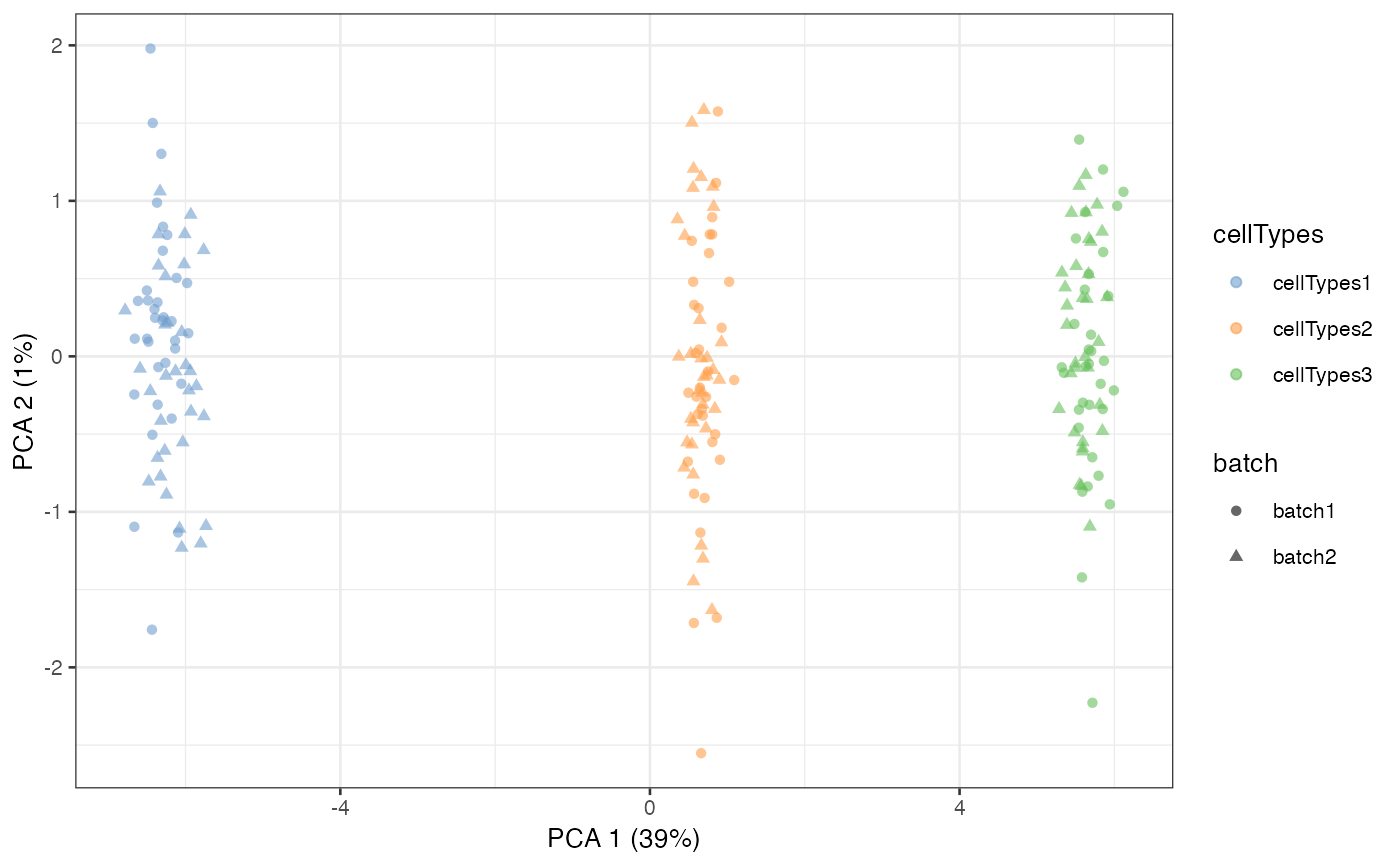
L = scater::runPCA(L, exprs_values = "logcounts")
scater::plotPCA(L, colour_by = 'cellTypes', shape = 'batch')
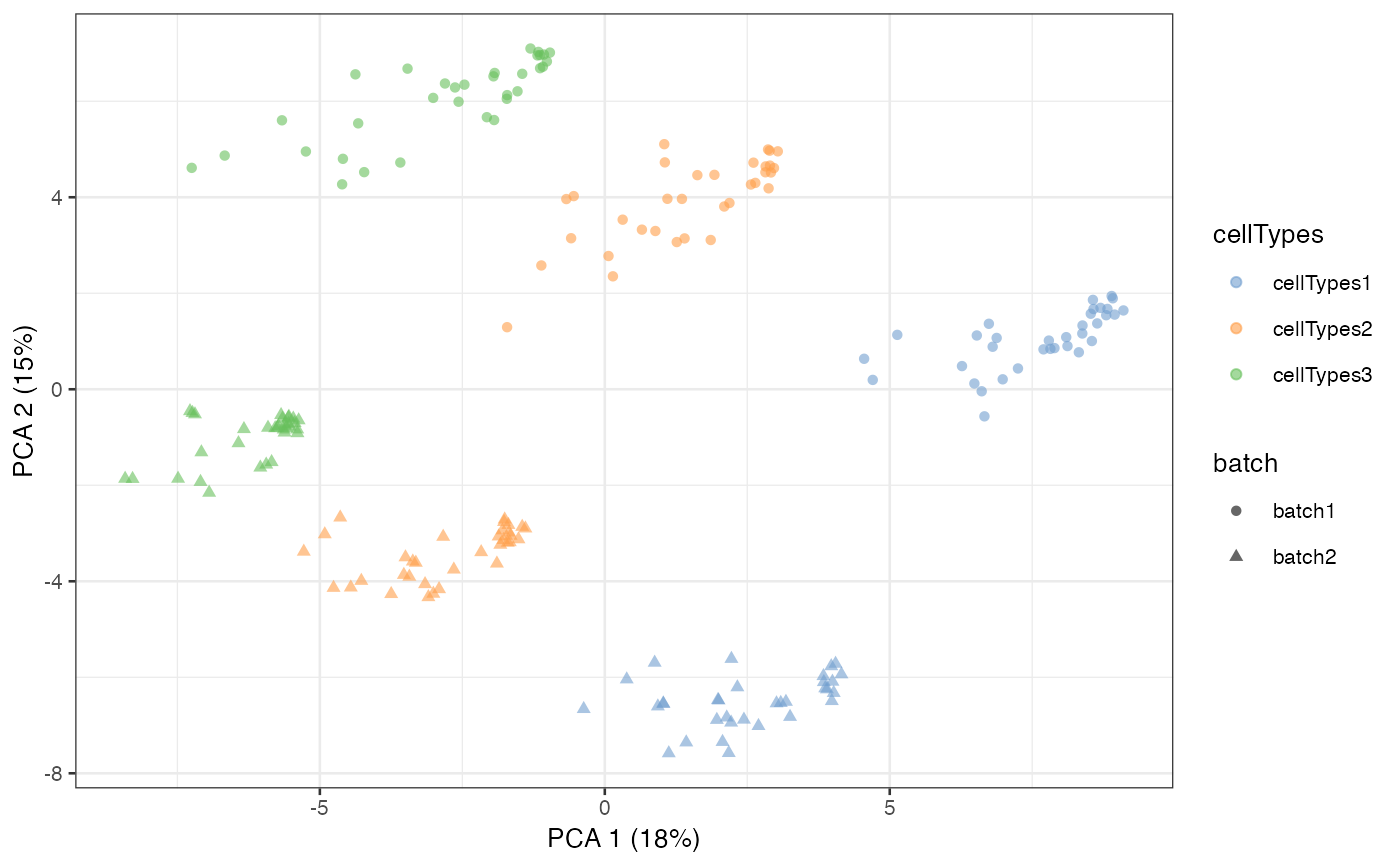 example = scater::runPCA(example, exprs_values = 'scMerge')
scater::plotPCA(example, colour_by = 'cellTypes', shape = 'batch')
example = scater::runPCA(example, exprs_values = 'scMerge')
scater::plotPCA(example, colour_by = 'cellTypes', shape = 'batch')