Overview of the BenchHub
28 January 2026
Source:vignettes/v00_overview_trio.Rmd
v00_overview_trio.Rmd
Introduction
BenchHub is a data storage framework implemented in R language to facilitate living benchmarks. It aims to enhance reproducibility and accessibility of benchmarking studies by making it easier to store, analyse and share benchmarking data.
The three components currently in BenchHub are:
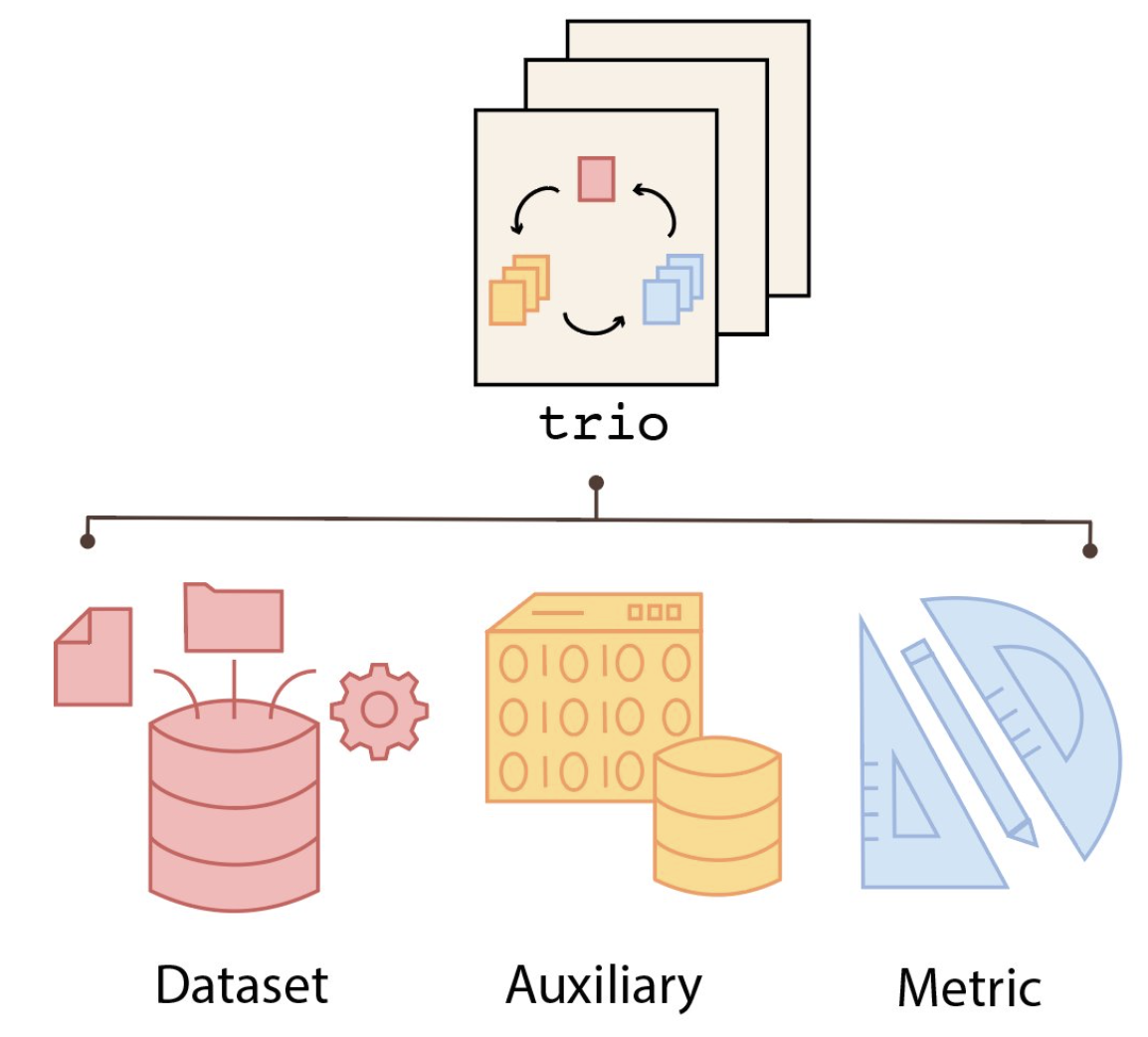
Trio: A data structure consisting of Dataset, Evidence and Metric to faciliate the sharing of benchmarking datasets within the community.
BenchmarkInsight: A data structure for storing benchmarking results and provides a collection of visualisations to faciliate the analysis of benchmarking results.
BenchmarkInsight: A data structure for storing collections of Trio objects and helper functions for specific benchmarking tasks.
BenchHub aims to make benchmarking easier for multiple groups of users in the community:
Benchmark Developers: BenchHub offers a central storage for contributing benchmarking studies with the community
Method Contributors: BenchHub allows evaluation of new tools against established benchmarks in the database without starting from scratch
Benchmark Consumers: BenchHub allows exploring and interpretation of results to make informed method selections
The Trio Framework
Trio is built around three key components:
Data: Data used by the methods to generate
output.
Supporting Evidence: Metadata to compare with the
output of methods, such as cell type, patient outcome, disease
pathway.
Metric: Evaluation metrics used to compare output of
methods with supporting evidence.
Trio is implemented as R6 object with fields to store each of the components.
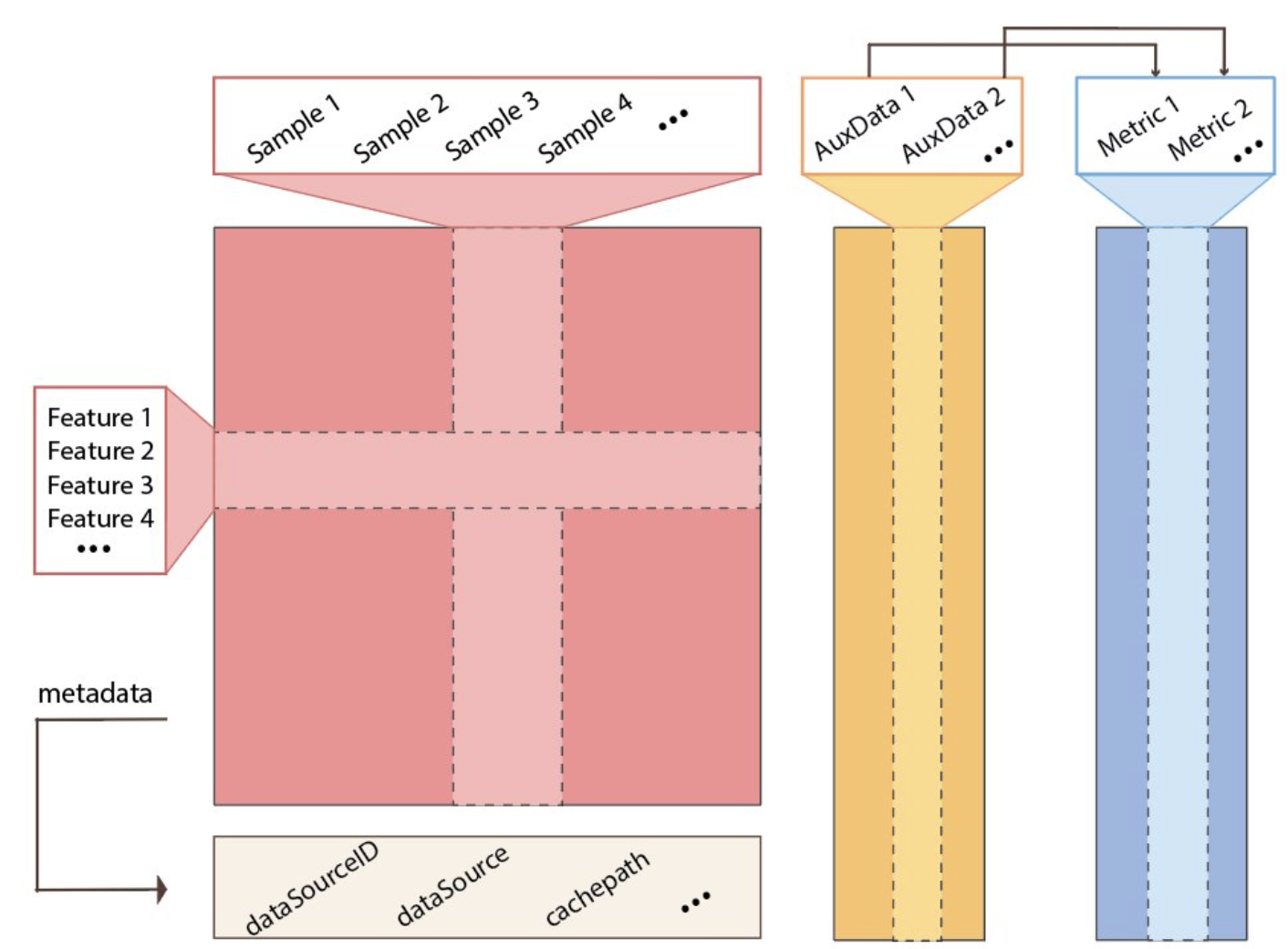
BenchmarkInsight
BenchmarkInsight serves as a visualisation and analysis tool for benchmarking results. It contains multiple visualisation techniques to help researchers analyse benchmarking results in terms of data, methods and metrics.
Once results are evaluated using Trio, the output can be directly passed into the benchmarkInsight object. BenchmarkInsight currently supports the following plot types.
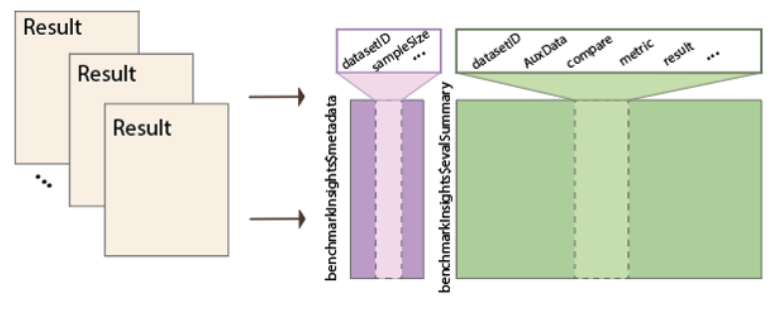
BenchmarkStudy
Benchmarking often involve large amount of datasets and processing scripts. BenchmarkStudy serves as the organisation framework for such objects. It stores references to collections of Trio objects and helper functions that standardise method outputs into a common form to evaluation.
## R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
## Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
## Running under: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
## LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.26.so; LAPACK version 3.12.0
##
## locale:
## [1] LC_CTYPE=C.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=C.UTF-8
## [4] LC_COLLATE=C.UTF-8 LC_MONETARY=C.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=C.UTF-8
## [7] LC_PAPER=C.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C LC_ADDRESS=C
## [10] LC_TELEPHONE=C LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
##
## time zone: UTC
## tzcode source: system (glibc)
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] BiocStyle_2.38.0
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] digest_0.6.39 desc_1.4.3 R6_2.6.1
## [4] bookdown_0.46 fastmap_1.2.0 xfun_0.56
## [7] cachem_1.1.0 knitr_1.51 htmltools_0.5.9
## [10] rmarkdown_2.30 lifecycle_1.0.5 cli_3.6.5
## [13] sass_0.4.10 pkgdown_2.2.0 textshaping_1.0.4
## [16] jquerylib_0.1.4 systemfonts_1.3.1 compiler_4.5.2
## [19] tools_4.5.2 ragg_1.5.0 bslib_0.10.0
## [22] evaluate_1.0.5 yaml_2.3.12 BiocManager_1.30.27
## [25] jsonlite_2.0.0 rlang_1.1.7 fs_1.6.6
## [28] htmlwidgets_1.6.4