Performing scClassify using pretrained model
Yingxin Lin
School of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Sydney, Australia22 April 2020
Source:vignettes/pretrainedModel.Rmd
pretrainedModel.RmdIntroduction
A common application of single-cell RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data is to identify discrete cell types. To take advantage of the large collection of well-annotated scRNA-seq datasets, scClassify package implements a set of methods to perform accurate cell type classification based on ensemble learning and sample size calculation.
This vignette will provide an example showing how users can use a pretrained model of scClassify to predict cell types. A pretrained model is a scClassifyTrainModel object returned by train_scClassify(). A list of pretrained model can be found in https://sydneybiox.github.io/scClassify/index.html.
First, install scClassify, install BiocManager and use BiocManager::install to install scClassify package.
# installation of scClassify if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) { install.packages("BiocManager") } BiocManager::install("scClassify")
Setting up the data
We assume that you have log-transformed (size-factor normalized) matrices as query datasets, where each row refers to a gene and each column a cell. For demonstration purposes, we will take a subset of single-cell pancreas datasets from one independent study (Wang et al.).
library(scClassify) data("scClassify_example") wang_cellTypes <- scClassify_example$wang_cellTypes exprsMat_wang_subset <- scClassify_example$exprsMat_wang_subset exprsMat_wang_subset <- as(exprsMat_wang_subset, "dgCMatrix")
Here, we load our pretrained model using a subset of the Xin et al. human pancreas dataset as our reference data.
First, let us check basic information relating to our pretrained model.
data("trainClassExample_xin") trainClassExample_xin #> Class: scClassifyTrainModel #> Model name: training #> Feature selection methods: limma #> Number of cells in the training data: 674 #> Number of cell types in the training data: 4
In this pretrained model, we have selected the genes based on Differential Expression using limma. To check the genes that are available in the pretrained model:
features(trainClassExample_xin) #> [1] "limma"
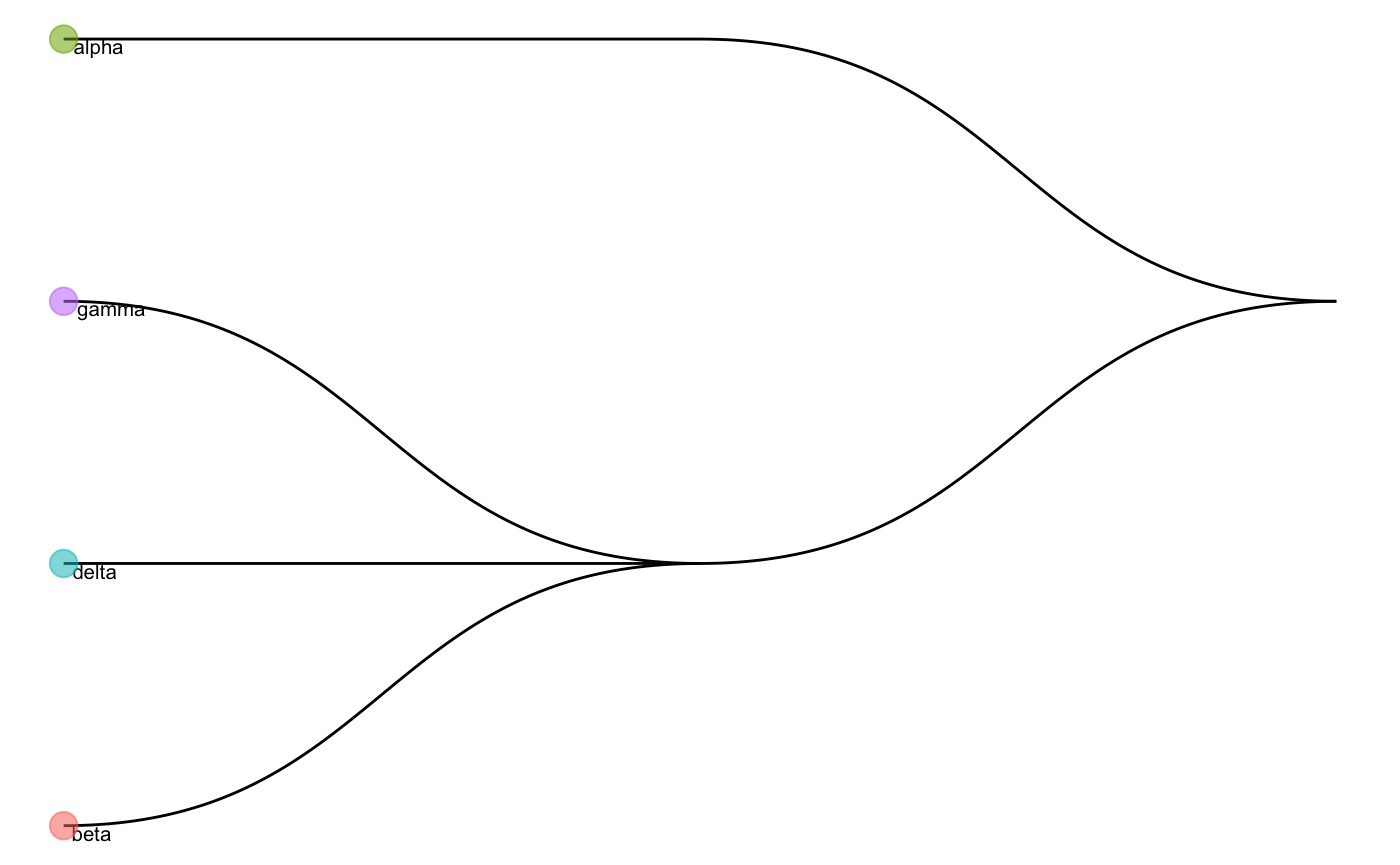
We can also visualise the cell type tree of the reference data.
plotCellTypeTree(cellTypeTree(trainClassExample_xin))
Running scClassify
Next, we perform predict_scClassify with our pretrained model trainRes = trainClassExample to predict the cell types of our query data matrix exprsMat_wang_subset_sparse. Here, we used pearson and spearman as similarity metrics.
pred_res <- predict_scClassify(exprsMat_test = exprsMat_wang_subset, trainRes = trainClassExample_xin, cellTypes_test = wang_cellTypes, algorithm = "WKNN", features = c("limma"), similarity = c("pearson", "spearman"), prob_threshold = 0.7, verbose = TRUE) #> Performing unweighted ensemble learning... #> Using parameters: #> similarity algorithm features #> "pearson" "WKNN" "limma" #> [1] "Using dynamic correlation cutoff..." #> [1] "Using dynamic correlation cutoff..." #> classify_res #> correct correctly unassigned intermediate #> 0.704590818 0.239520958 0.000000000 #> incorrectly unassigned error assigned misclassified #> 0.000000000 0.051896208 0.003992016 #> Using parameters: #> similarity algorithm features #> "spearman" "WKNN" "limma" #> [1] "Using dynamic correlation cutoff..." #> [1] "Using dynamic correlation cutoff..." #> classify_res #> correct correctly unassigned intermediate #> 0.702594810 0.013972056 0.000000000 #> incorrectly unassigned error assigned misclassified #> 0.001996008 0.277445110 0.003992016 #> weights for each base method: #> numeric(0)
Noted that the cellType_test is not a required input. For datasets with unknown labels, users can simply leave it as cellType_test = NULL.
Prediction results for pearson as the similarity metric:
table(pred_res$pearson_WKNN_limma$predRes, wang_cellTypes) #> wang_cellTypes #> acinar alpha beta delta ductal gamma stellate #> alpha 0 206 0 0 0 2 0 #> beta 0 0 118 0 1 0 0 #> beta_delta_gamma 0 0 0 0 25 0 0 #> delta 0 0 0 10 0 0 0 #> gamma 0 0 0 0 0 19 0 #> unassigned 5 0 0 0 70 0 45
Prediction results for spearman as the similarity metric:
table(pred_res$spearman_WKNN_limma$predRes, wang_cellTypes) #> wang_cellTypes #> acinar alpha beta delta ductal gamma stellate #> alpha 0 206 0 0 0 2 2 #> beta 2 0 118 0 29 0 6 #> beta_delta_gamma 1 0 0 0 66 0 31 #> delta 0 0 0 10 0 0 2 #> gamma 0 0 0 0 0 18 0 #> unassigned 2 0 0 0 1 1 4
Session Info
sessionInfo() #> R Under development (unstable) (2020-03-25 r78063) #> Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit) #> Running under: macOS Catalina 10.15.4 #> #> Matrix products: default #> BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib #> LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib #> #> locale: #> [1] en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8/C/en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8 #> #> attached base packages: #> [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base #> #> other attached packages: #> [1] scClassify_0.99.2 BiocStyle_2.15.6 #> #> loaded via a namespace (and not attached): #> [1] Biobase_2.47.3 viridis_0.5.1 mixtools_1.2.0 #> [4] tidyr_1.0.2 tidygraph_1.1.2 viridisLite_0.3.0 #> [7] splines_4.0.0 ggraph_2.0.2 RcppParallel_5.0.0 #> [10] assertthat_0.2.1 statmod_1.4.34 BiocManager_1.30.10 #> [13] stats4_4.0.0 yaml_2.2.1 ggrepel_0.8.2 #> [16] pillar_1.4.3 backports_1.1.6 lattice_0.20-41 #> [19] glue_1.4.0 limma_3.43.5 digest_0.6.25 #> [22] polyclip_1.10-0 colorspace_1.4-1 htmltools_0.4.0 #> [25] Matrix_1.2-18 pkgconfig_2.0.3 bookdown_0.18 #> [28] purrr_0.3.3 scales_1.1.0 tweenr_1.0.1 #> [31] hopach_2.47.0 BiocParallel_1.21.2 ggforce_0.3.1 #> [34] proxy_0.4-23 tibble_3.0.0 mgcv_1.8-31 #> [37] farver_2.0.3 ggplot2_3.3.0 ellipsis_0.3.0 #> [40] BiocGenerics_0.33.3 cli_2.0.2 survival_3.1-12 #> [43] magrittr_1.5 crayon_1.3.4 memoise_1.1.0 #> [46] evaluate_0.14 fs_1.4.1 fansi_0.4.1 #> [49] nlme_3.1-145 MASS_7.3-51.5 segmented_1.1-0 #> [52] tools_4.0.0 minpack.lm_1.2-1 lifecycle_0.2.0 #> [55] stringr_1.4.0 kernlab_0.9-29 S4Vectors_0.25.15 #> [58] munsell_0.5.0 cluster_2.1.0 compiler_4.0.0 #> [61] pkgdown_1.5.1.9000 proxyC_0.1.5 rlang_0.4.5 #> [64] grid_4.0.0 rstudioapi_0.11 igraph_1.2.5 #> [67] labeling_0.3 rmarkdown_2.1 gtable_0.3.0 #> [70] graphlayouts_0.6.0 R6_2.4.1 gridExtra_2.3 #> [73] knitr_1.28 dplyr_0.8.5 rprojroot_1.3-2 #> [76] desc_1.2.0 stringi_1.4.6 parallel_4.0.0 #> [79] Rcpp_1.0.4.6 vctrs_0.2.4 diptest_0.75-7 #> [82] tidyselect_1.0.0 xfun_0.12